If you’ve ever experienced sudden abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting, it could be a sign of gallbladder stones. These small, hard deposits can cause significant discomfort and may require medical intervention. In this blog, we’ll break down everything you need to know about gallbladder stones—what they are, how they form, the common symptoms, and the treatment options available. Dr. Nishant Kurian explains all this and more in his insightful video, which can help you better understand this common condition.
What Are Gallbladder Stones?
Gallbladder stones, also known as gallstones, are small, hard particles that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver. The gallbladder stores bile, a fluid produced by the liver that helps in digesting fats. When the balance of substances in bile is disrupted—such as having too much cholesterol or waste—gallstones can develop. There are two main types:
- Cholesterol Stones: These are the most common type and are usually yellowish.
- Pigment Stones: These are smaller and darker and occur when there’s too much bilirubin (a waste product of red blood cells) in the bile.
Common Symptoms of Gallbladder Stones
Gallstones may not always show symptoms. In fact, many people live with them without even knowing. However, when symptoms do appear, they can be quite uncomfortable. Common signs of gallbladder stones include:
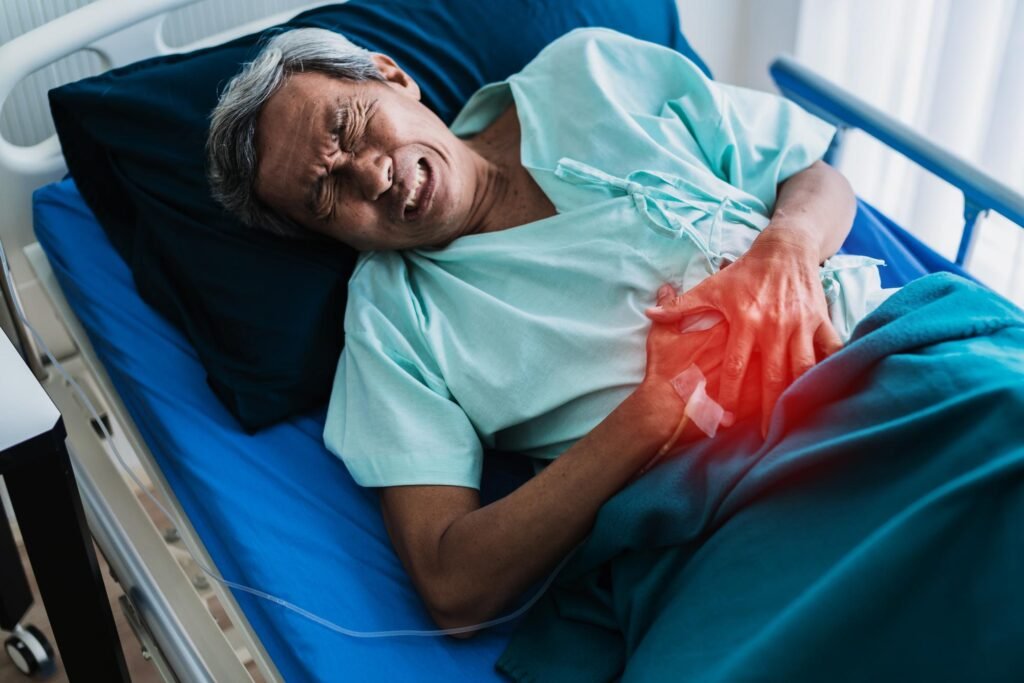
- Abdominal Pain: Often sharp and sudden, the pain is typically felt in the upper right side of the abdomen and can last for several minutes to hours.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Due to digestive disruption, nausea or vomiting may occur.
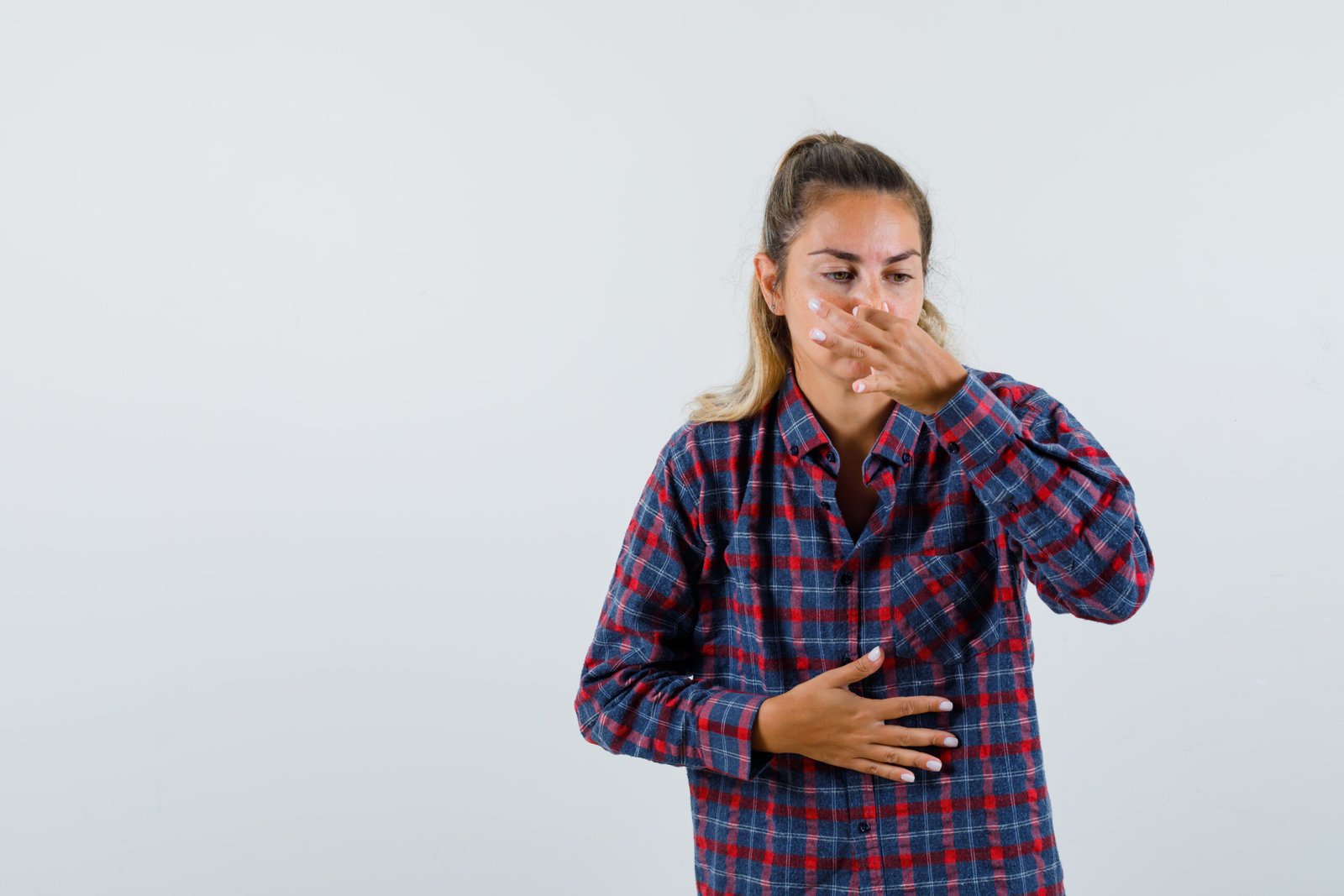
- Indigestion: You may experience bloating, gassiness, or acid reflux after eating.
- Jaundice: If a gallstone blocks the bile duct, it can cause a yellowing of the skin and eyes, which is known as jaundice.
If you experience these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider to determine whether gallstones are the cause.
What Causes Gallbladder Stones?
There are several factors that contribute to the formation of gallstones. Dr. Nishant Kurian points out that lifestyle and genetics play a significant role:
- High Cholesterol Levels: Excess cholesterol in bile can lead to the formation of cholesterol stones.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the risk, as it can cause an imbalance in bile composition.
- Age: Gallstones are more common in people over 40.
- Family History: A genetic predisposition can increase the likelihood of developing gallstones.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy may raise the risk.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are also more prone to gallstones, as they often have higher levels of cholesterol in their blood.
Understanding these risk factors can help you take proactive steps to prevent gallstones from developing.
Treatment Options for Gallbladder Stones
When it comes to treating gallstones, there are several options, depending on the severity of your symptoms and the size of the stones. Dr. Nishant Kurian explains the different treatment methods:
- Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Medications: In some cases, medications that help dissolve the gallstones may be prescribed. However, this treatment is typically only effective for small stones and can take months or even years.
- Shockwave Therapy (Lithotripsy): This method uses sound waves to break the stones into smaller pieces that can then pass through the bile ducts more easily.
- Medications: In some cases, medications that help dissolve the gallstones may be prescribed. However, this treatment is typically only effective for small stones and can take months or even years.
- Surgical Treatment:
- Cholecystectomy: This is the most common and effective treatment for gallstones. It involves the surgical removal of the gallbladder, usually through a minimally invasive laparoscopic procedure. Laparoscopic surgery involves smaller incisions, a shorter recovery time, and less pain compared to traditional open surgery.
- Cholecystectomy: This is the most common and effective treatment for gallstones. It involves the surgical removal of the gallbladder, usually through a minimally invasive laparoscopic procedure. Laparoscopic surgery involves smaller incisions, a shorter recovery time, and less pain compared to traditional open surgery.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP):
- If a gallstone blocks the bile duct, an ERCP procedure can be performed to remove the stone or clear the blockage, often without the need for open surgery.
- If a gallstone blocks the bile duct, an ERCP procedure can be performed to remove the stone or clear the blockage, often without the need for open surgery.
Preventing Gallstones
While some risk factors—like age and family history—are beyond your control, there are a few lifestyle changes you can make to lower your risk of developing gallstones:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help reduce the risk. Avoid high-cholesterol and fatty foods.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of gallstones, so maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise is key.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain proper bile consistency and can support digestion.
- Avoid Rapid Weight Loss: Losing weight too quickly can actually increase the risk of gallstones. Aim for gradual weight loss through a healthy diet and exercise.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you suspect you have gallstones or are experiencing symptoms like persistent abdominal pain, nausea, or jaundice, it’s essential to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis. Early detection and treatment can help prevent complications like gallbladder inflammation or infection.
Conclusion
Gallbladder stones are a common health issue that can cause significant discomfort if left untreated. Whether you experience mild symptoms or need surgery, there are effective treatments available. Dr. Nishant Kurian’s video offers valuable insights into gallbladder stones, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. By understanding this condition and taking proactive steps to maintain a healthy lifestyle, you can reduce your risk and ensure better digestive health.
For a deeper understanding of gallbladder stones and treatment options, be sure to watch the full video by Dr. Nishant Kurian:
Watch the video here